
Dr. ROY MEDICAL HALL
Jaffer Khan Colony | Calicut | Kerala | IndiaSexologist Doctor - Sexology Clinic
+91 9349113791
Established in 1960

Dr. ROY MEDICAL HALL
Jaffer Khan Colony | Calicut | Kerala | IndiaSexologist Doctor - Sexology Clinic
+91 9349113791
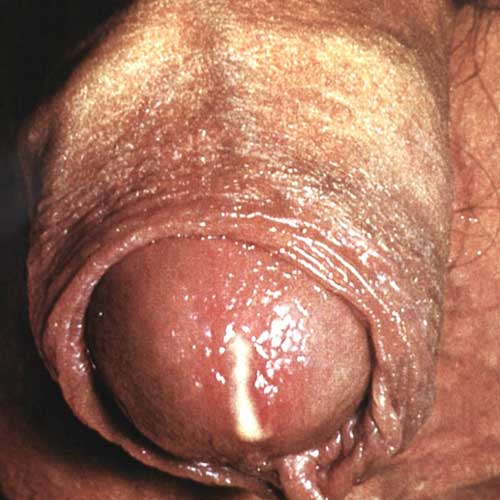 Gonorrhea, a highly contagious sexually transmitted disease (STD), is one of the most common STDs, sometimes referred to as "the clap," gonorrhea may produce signs and symptoms such as a burning sensation when urinating or a thick discharge from the penis or vagina. Many people experience mild or no signs or symptoms. Left untreated, gonorrhea can cause serious complications, especially in women.
Gonorrhea, a highly contagious sexually transmitted disease (STD), is one of the most common STDs, sometimes referred to as "the clap," gonorrhea may produce signs and symptoms such as a burning sensation when urinating or a thick discharge from the penis or vagina. Many people experience mild or no signs or symptoms. Left untreated, gonorrhea can cause serious complications, especially in women.
CAUSES
.jpg) The cause of gonorrhea is a bacterium (also referred to as gonococcus) that spreads through sexual contact. The disease can pass from a mother to her child during birth.
The cause of gonorrhea is a bacterium (also referred to as gonococcus) that spreads through sexual contact. The disease can pass from a mother to her child during birth.
The bacterium is spread through semen or vaginal fluids during unprotected sexual contact, heterosexual or homosexual, with an infected partner.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Signs and symptoms of gonorrhea may include: -
Thick, cloudy, or bloody discharge from the penis or vagina
Pain or burning sensation when urinating
Frequent urination
Pain during sexual intercourse
.jpg) The first gonorrhea symptoms generally appear within two to 10 days after exposure to the bacterium. However, some people may be infected for months before signs or symptoms occur.
The first gonorrhea symptoms generally appear within two to 10 days after exposure to the bacterium. However, some people may be infected for months before signs or symptoms occur.
HOW GONORRHOEA AFFECTS MEN
.jpg) In men, first, there's often a tingling sensation in the urethra, the passageway that carries urine from your bladder to the outside of your body. Later, urination becomes painful and you may notice a discharge from your penis. As the infection progresses, urethral pain usually becomes more pronounced and the discharge becomes more profuse and thick.
In men, first, there's often a tingling sensation in the urethra, the passageway that carries urine from your bladder to the outside of your body. Later, urination becomes painful and you may notice a discharge from your penis. As the infection progresses, urethral pain usually becomes more pronounced and the discharge becomes more profuse and thick.
HOW GONORRHOEA AFFECTS WOMEN
.jpg) In women, the signs and symptoms, if any, may be so mild that you may not realize you have the infection. Often, the only clue that you may have gonorrhea comes when someone with who you've had sexual contact develops the disease. The infection usually affects the cervix and other reproductive organs as well as the urethra. In some women, gonorrhea causes frequent, urgent, and painful urination along with an abnormal discharge from the vagina or urethra.
In women, the signs and symptoms, if any, may be so mild that you may not realize you have the infection. Often, the only clue that you may have gonorrhea comes when someone with who you've had sexual contact develops the disease. The infection usually affects the cervix and other reproductive organs as well as the urethra. In some women, gonorrhea causes frequent, urgent, and painful urination along with an abnormal discharge from the vagina or urethra.
COMPLICATIONS
Not receiving adequate treatment for gonorrhea may lead to complications. These may include: -
.jpg) Inflammation of the epididymis. In men, epididymitis — inflammation of the rear portion of the testicles where the sperm ducts are located (epididymis) — is an acute condition treatable with antibiotics and pain relievers. If untreated, it may lead to infertility.
Inflammation of the epididymis. In men, epididymitis — inflammation of the rear portion of the testicles where the sperm ducts are located (epididymis) — is an acute condition treatable with antibiotics and pain relievers. If untreated, it may lead to infertility.
Pelvic inflammatory disease. In women, the bacteria can spread into the uterus and fallopian tubes, causing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which may result in scarring of the tubes, a greater risk of ectopic pregnancy, and infertility. PID may lead to abdominal pain, backache, irregular menstrual periods, pain during intercourse, and foul-smelling vaginal discharge. It's a serious infection that requires immediate treatment by a doctor.
The spread of the infection during childbirth. A pregnant woman with untreated gonorrhea may spread the infection to her baby as the baby passes through the birth canal during delivery. In an infant, gonorrhea may cause complications such as blindness and widespread infection of the joints and blood.
Anorectal gonorrhea. In both sexes, anorectal gonorrhea may result from anal intercourse with an infected person or the infection spreading from the genital area. It may cause some discomfort in and discharge from the anal area, but in many cases no signs or symptoms are present.
Irritation of your throat and tonsils. Oral sex can lead to pharyngeal gonorrhea with a sore throat, pain in swallowing, and redness of the throat and tonsils.
Eye inflammation. Infection may sometimes spread to the eye by touching or rubbing the eye with your hand after it has been in contact with the infected discharge. Gonorrhea in such cases can cause a red, inflamed eye (conjunctivitis). In babies who contract gonorrhea during childbirth, gonorrhea eye infections can lead to blindness.
Widespread infection in your body. Rarely, the bacterium that causes gonorrhea can spread through the bloodstream to cause infection in other parts of your body. Fever, rash, skin sores, joint pain, swelling, and stiffness are possible results.
PREVENTION
To prevent the spread of gonorrhea, use latex condoms and avoid oral sex.
Gonorrhea is highly contagious and yet may cause no signs or symptoms.
The more sexual partners you have, the greater your risk, of casual contact.
WHEN TO SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE
Have a discharge from your vagina, or penis, or have other signs and symptoms of gonorrhea.
Are concerned that a partner may have been exposed to the infection.
Gonorrhea has been diagnosed in a partner.
MOBILE
+91 93491 13791
+91 88484 73488
|
Click for Online Consultation Form
|